- Home Page
- Company Profile
-
Our Products
- Aromatic Hydrocarbon Solvents
- De Aromatize Hydrocarbon Solvents
- Aliphatic Hydrocarbon Solvents
- Cyclo Hexane Solvent
- Drilling Oils - Fluids
- Superior Kerosene Oil
- Mining Oil
- Mineral Turpentine Oil -MTO
- Hexane Solvent
- Slop Oil
- Aluminium Rolling Oil
- Heptane Solvent
- Nitrobenzene Chemical Structure
- MIBK (Methyl Isobutyl Ketone)
- MEA (Monoethanolamine)
- MDC (Methylene Dichloride - Dichloromethane)
- Low Aromatic White Spirit (LAWS)
- LDO (Light Diesel Oils)
- LABSA (Linear Alkyl Benzene Sulphonic Acid)
- Iso Propyl Alcohol
- DMSO (Dimethyl Sulfoxide)
- Butyl Cellosolve (Ethylene Glycol Monobutyl Ether)
- Butyl Acetate
- Benzene Chemical Structure
- Octanol Chemical Structure
- Rubber Process Oil
- Glycols
- Petroleum Ether
- Base Oils
- Deodorised Kerosene (DOK)
- Organic Solvents
- Industrial Oil
- Contact Us
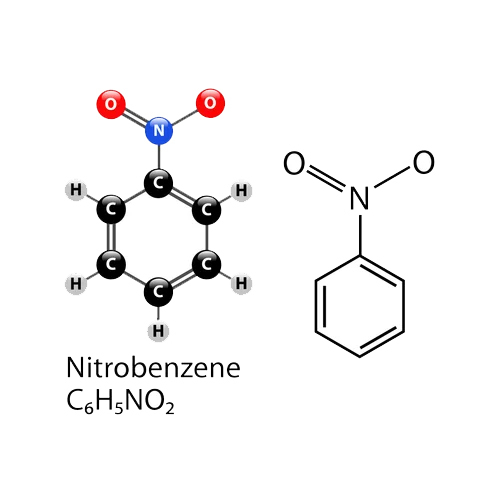
Nitrobenzene Chemical Structure
Product Details:
- Density 1.20 Gram per cubic centimeter(g/cm3)
- Odour Almond-like, bitter odor
- Appearance Pale yellow to brown oily liquid
- Molecular Weight 123.11 g/mol
- Storage Instructions Store in tightly closed containers, in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area, away from light and oxidizing agents
- Solubility Slightly soluble in water, miscible with organic solvents
- Ph Level Not applicable (neutral organic compound)
- Click to view more
X
Nitrobenzene Chemical Structure Price And Quantity
- 1 Drum
- 5.7°C
- 482°C
- 1662
- 210.9°C
- 1.552 at 20°C
- Toxic, Harmful, Environmental Hazard
- C6H5NO2
- 88°C (closed cup)
- 0.245 mm Hg at 25°C
- Stable under recommended storage conditions
Nitrobenzene Chemical Structure Product Specifications
- 24 months from date of manufacturing
- Almond-like, bitter odor
- Intermediate for aniline production, dyes, lubricating oils, pesticides, solvents
- 98-95-3
- Liquid
- Not applicable (neutral organic compound)
- 99
- Pale yellow to brown oily liquid
- 2 years (under recommended storage conditions)
- 123.11 g/mol
- Other
- Chemical industry, pharmaceutical synthesis, perfumery
- Slightly soluble in water, miscible with organic solvents
- 1.20 Gram per cubic centimeter(g/cm3)
- Benzene (nitration)
- Store in tightly closed containers, in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area, away from light and oxidizing agents
- Nitrobenzol; Oil of Mirbane; Nitrobenzolum
- Aromatic Nitrogen Compound
- Industrial synthesis, chemical manufacturing processes
- Nitrobenzene
- 5.7°C
- 482°C
- 1662
- 210.9°C
- 1.552 at 20°C
- Toxic, Harmful, Environmental Hazard
- C6H5NO2
- 88°C (closed cup)
- 0.245 mm Hg at 25°C
- Stable under recommended storage conditions
Nitrobenzene Chemical Structure Trade Information
- 5000 Drum Per Month
- 2-10 Days
Product Description
An aromatic solvent and intermediate primarily used for aniline production and in pesticides.
Applications:
- Aniline and rubber chemicals
- Pesticide manufacturing
- Solvent in industrial processes
- Dye and chemical synthesis
Key Physical Properties of Nitrobenzene
Nitrobenzene is a liquid at room temperature, with a density of 1.20 g/cm3 and a molecular weight of 123.11 g/mol. It features a refractive index of 1.552 (at 20C), slight solubility in water, and is miscible with most organic solvents. Its melting and boiling points are 5.7C and 210.9C respectively, while its flash point and autoignition temperature are 88C and 482C, highlighting important safety considerations.
Industrial Applications and Uses
Nitrobenzene is extensively utilized as a precursor in the synthesis of aniline, dyes, lubricating oils, pesticides, and solvents. Its versatility makes it a vital raw material for the chemical and pharmaceutical industries, as well as in perfumery due to its distinctive aroma. Typically processed through industrial synthesis and chemical manufacturing, nitrobenzene is an essential component in various commercial operations.
Handling and Storage Guidelines
For safe handling, nitrobenzene should be stored in tightly closed containers within a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area, away from direct light and oxidizing substances. It remains stable under recommended storage conditions and has a shelf life of two years. Due to its classification as toxic and environmentally harmful, appropriate protective measures are necessary during storage and handling.
FAQ's of Nitrobenzene Chemical Structure:
Q: How is nitrobenzene produced and what is its principal raw material?
A: Nitrobenzene is synthesized via the nitration of benzene, where benzene serves as the primary raw material. This process involves the reaction of benzene with concentrated nitric acid and sulfuric acid under controlled conditions.Q: What are the main uses of nitrobenzene in the chemical industry?
A: Nitrobenzene is mainly used as an intermediate for producing aniline, dyes, lubricating oils, pesticides, and solvents. It also finds usage in pharmaceutical synthesis and perfumery due to its characteristic almond-like aroma.Q: When should nitrobenzene be replaced or disposed of based on its shelf life?
A: Nitrobenzene should ideally be used or appropriately disposed of within two years (24 months) from its manufacturing date to ensure maximum quality and performance.Q: Where should nitrobenzene be stored to maintain its stability?
A: Nitrobenzene needs to be stored in tightly closed containers in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area, away from direct sunlight and incompatible materials like oxidizing agents to keep it stable.Q: What safety precautions must be taken when handling nitrobenzene?
A: Because nitrobenzene is classified as toxic and an environmental hazard, handlers should wear suitable protective gear, use proper ventilation, and avoid direct contact or inhalation. Emergency facilities and procedures should be accessible in case of spills or exposure.Q: How does the chemical structure of nitrobenzene contribute to its industrial application?
A: Nitrobenzene's aromatic ring and nitro group facilitate its use as a starting material for various chemical reactions, particularly in aniline synthesis, making it an indispensable intermediate in multiple industrial processes.Tell us about your requirement

Price:
Quantity
Select Unit
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
Additional detail
Mobile number
Email







 Call Me Free
Call Me Free
